Homes and Condos for Sale and Rent in Miami
Integrated Services 360° 360°
Our apartments portfolio
Our houses portfolio
Projects in Orlando
Find your property in Miami
We have a wide portfolio of properties that are perfect for you
2,000 clients from around the world have invested in Miami thanks to PFS
22 years of experience in property sales in the United States
Our long-standing track record as leaders in the Miami real estate market positions us as your best choice. We have a proven track record that backs our reliable service and successful results.
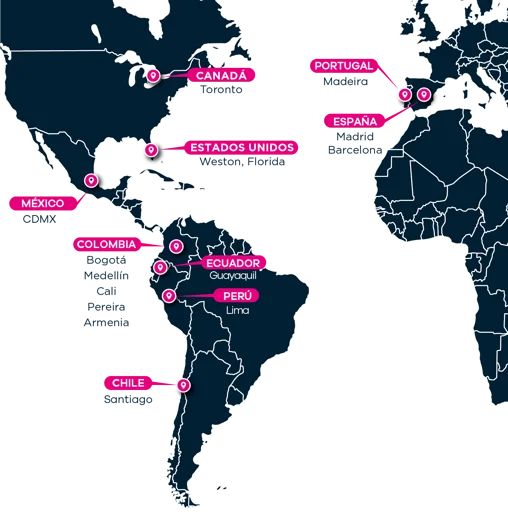
65 advisors in 12 countries in the Americas and Europe
A wide network of 65 advisors strategically located in the Americas and Europe to maximize your real estate investment opportunities.
More than 2,000 satisfied customers trust us
With an international network of agents, we offer global and localized perspectives that enhance our ability to find unmatched opportunities. From advice to closing the deal, we optimize your real estate investment opportunities.